The transition to hybrid IT architectures and remote work strategies has greatly expanded the IT estates of most organizations in recent years. Couple this expansion with the growing number of computing and IoT devices that connect to company networks today and you understand why cybersecurity is a growing challenge: As your IT footprint grows, so does your attack surface.
Reducing that attack surface requires far more than just regular patching of your software and hardware systems to remediate critical flaws. To protect your infrastructure, users and sensitive information from cyber threats, you need a comprehensive vulnerability management program that includes asset discovery, vulnerability scans, and prioritization and remediation of identified vulnerabilities.
This article outlines five best practices for any vulnerability management program. Note that vulnerability management isn’t a once-and-done process. To be effective, it must be a regular routine that is assigned to designated IT personnel.
1. Asset Discovery
You can’t secure what you don’t know about, so the first step in vulnerability management is to initiate a discovery scan to establish a full list of every device in your environment. This scanning should include everything from domain controllers and application servers to small things like IoT sensors and mounted cameras. Internal testing and DevOps environments need to be included as well because any connected device is vulnerable to security threats.
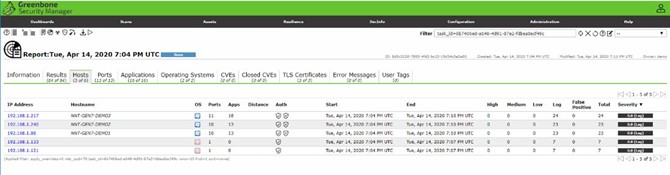
The initial discovery effort needs to be followed by scheduled scans on a regular basis to ensure accurate reporting of all assets, including new devices introduced to your network. Scans should be scheduled at different times of the day, since different work schedules may mean that some devices are connected only during certain times. There are multiple vulnerability scanning tools on the market that you can leverage. The screenshot below shows a discovery report from Greenbone Enterprise.
2. Scanning Frequency
How often should you scan your network? The Center for Internet Security (CIS) recommends that organizations perform scanning every two weeks. Environments with a highly dynamic user base, such as educational institutions, may want to run weekly or even daily scans, while smaller and more static organizations may find that one scan each month is sufficient. While there is no right answer, you should err on the side of caution because asset discovery scans will have little impact on network performance.
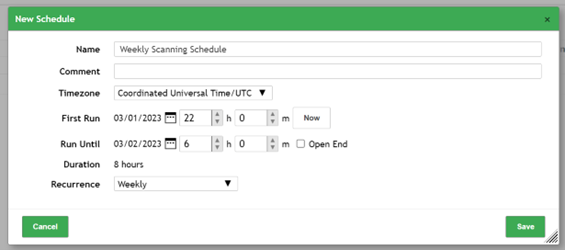
Here is an example of how you can set up a scheduled scan in Greenbone Enterprise:
3. Running Vulnerability Scans
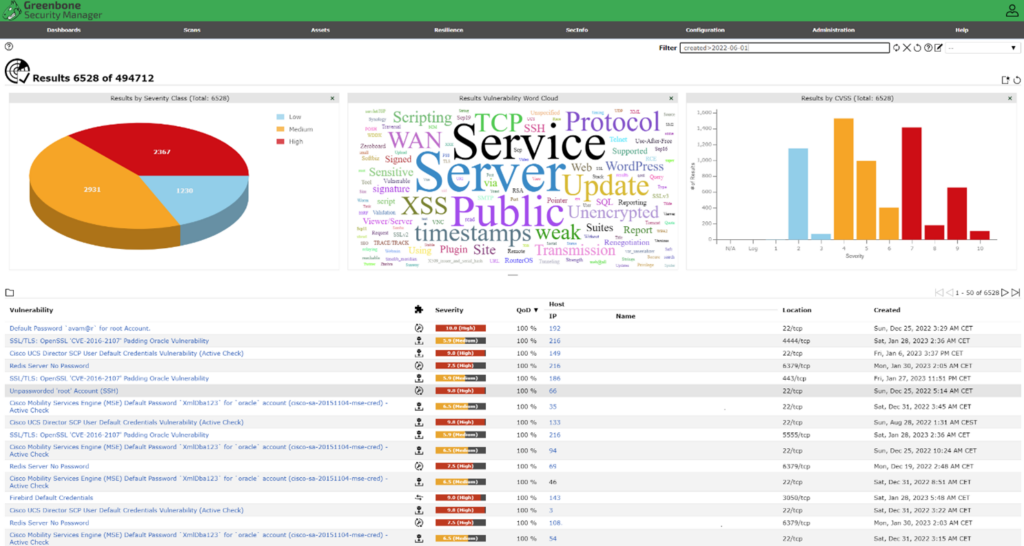
Of course, it’s not enough to simply inventory your IT systems; you also need to regularly scan all assets for vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. Unlike discovery scans, vulnerability scans can significantly impact system performance and they will take more time per asset, so it is usually best to conduct vulnerability scans outside of normal business hours.
You may need to define separate scanning strategies to accommodate different asset types in your environment. For example, a file server will require a deeper scan than an IoT device. Most quality vulnerability scanners enable you to create different scanning profiles for reporting on different systems and applications. Be sure your tool uses an updated database to test for newly published vulnerabilities.
You can perform scans using different credentials to find vulnerabilities that are unique to certain user roles and privilege assignments. Note that privileged credentials are usually required for deep-dive scans.
4. Prioritizing Your Findings
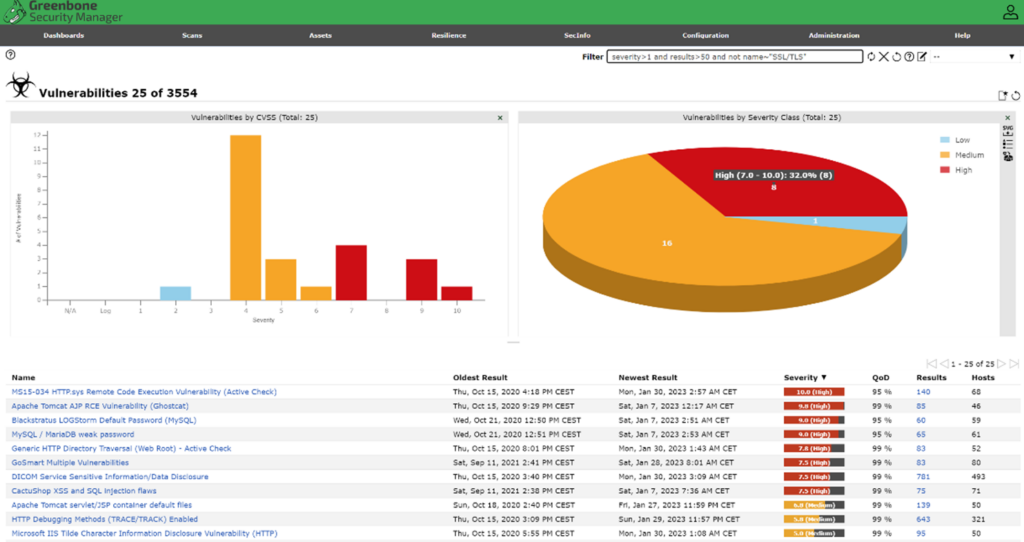
Vulnerability scanning reports often list many issues across multiple IT assets. Accordingly, IT teams need to prioritize their remediation efforts to ensure that the critical vulnerabilities are addressed promptly. While the report will generally provide a risk or severity rating, a good tool will enable you to filter and sort your results based on multiple factors, including the number of systems affected and how recently it appeared, so you can better leverage the information to quickly reduce risk.
5. Remediation
It is best practice to address any high-risk vulnerabilities first, regardless of where they appear in your network. In particular, do not put off remediation of serious issues in your development and testing environments; those systems can be especially vulnerable because they often have less restrictive policies.
Once your high-risk vulnerabilities are remediated, move on quickly to medium-risk vulnerabilities —hackers often target them because they know high-risk vulnerabilities will usually get addressed. After that, there are no hard and fast rules: Remediation should proceed based on your priorities. However, it’s usually wise to remediate any remaining vulnerabilities in your production systems first.
Once your remediation effort is complete, run a scan again to confirm that your systems are clean of vulnerabilities. Below is another example of a Greenbone Enterprise vulnerability report.
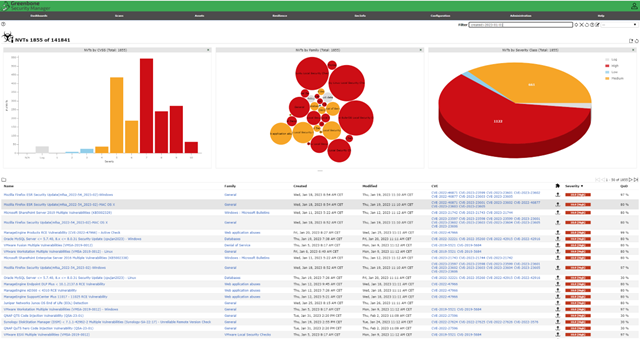
Conclusion
Vulnerability scanning software solutions are a vital part of any IT security strategy. They help organizations reduce their attack surface by identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities in the IT environment before they can be exploited. Moreover, a solid vulnerability management program helps ensure business continuity preventing disruptions and downtime in vital IT systems.


.png)